The Windows on Snapdragon Shift: A New Era for Windows PCs
The landscape of the Windows PC market is undergoing a seismic transformation, driven by advancements in Qualcomm Snapdragon chips and a strategic pivot away from Intel processors. This shift signifies a broader trend in computing, prioritizing energy efficiency, always-on connectivity, and enhanced AI capabilities.
Why Snapdragon?
Qualcomm’s Snapdragon processors have long been associated with smartphones and tablets, but their foray into the PC market has introduced compelling innovations. Snapdragon chips are built on ARM architecture, which is renowned for its low power consumption and high efficiency. This makes them ideal for ultra-portable laptops, hybrid devices, and enterprise solutions that demand long battery life without compromising performance.
In recent years, Microsoft has been aligning its hardware strategy with these trends. Devices powered by Snapdragon chips, such as the Surface Pro X, have showcased features like instant-on functionality, integrated 5G, and extended battery life—areas where traditional Intel chips have struggled to compete.
Microsoft’s Intel Breakup
In a move that surprised many industry observers, Microsoft announced it would no longer produce or sell devices powered by Intel processors. This decision underscores the company’s commitment to ARM-based platforms, signaling a significant shift in the PC ecosystem.
While Microsoft has not completely severed ties with Intel—Windows OS will continue to support x86 architecture—the departure from selling Intel-powered Surface devices speaks volumes about the company’s future direction. By focusing on Snapdragon, Microsoft aims to create tightly integrated hardware-software experiences similar to Apple’s successful M1 and M2 ecosystems.
The Benefits for Consumers
The transition to Snapdragon offers several advantages:
- Battery Efficiency: Snapdragon chips are optimized for long-lasting performance, often delivering up to 20 hours of usage on a single charge.
- 5G Connectivity: With native support for 5G, Snapdragon devices are future-proofed for next-generation wireless networks.
- AI-Driven Features: Snapdragon processors integrate advanced AI capabilities, enhancing tasks like video conferencing, image recognition, and voice assistants.
- Fanless Designs: The energy efficiency of ARM processors enables quieter, cooler, and slimmer devices.
Challenges and Transition Pain
Despite the potential, the shift to Snapdragon isn’t without challenges. Compatibility with legacy x86 applications remains a concern, although Microsoft and Qualcomm have made significant progress in emulation technology. Developers may also need time to optimize their software for ARM architecture fully.
What’s Next?
The Qualcomm-Microsoft partnership is poised to grow, especially with Qualcomm’s upcoming Oryon CPUs, which promise performance gains that rival traditional PC processors. This development is set to challenge Intel and AMD’s dominance, offering consumers and businesses alike a compelling alternative.
Same Story as with the Mac that happened in 2024
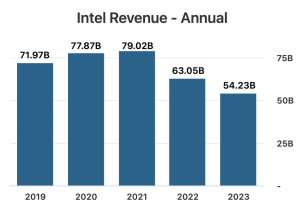
The Apple Macintosh underwent this transition 4 years ago, changing from Intel Chips to ARM based Apple Silicon Chips. This transition gave Mac users faster processing, enabled Apple’s transition to AI and longer battery life. Because of this Intel’s revenue has been on a downward slope as evidenced by their sales decline for the last 2 years.
If you are in the market for a new PC, it is probably best not to look for an Intel Inside sticker.